Every year more than 300 thousand new cases of brain tumors are diagnosed worldwide, according to data from the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM). Also, these tumors correspond to 2.5 percent of cancer mortality. However, experts at Houston Methodist Hospital say that, thanks to scientific advances, patients with brain tumors can have hope because of scientific advances.
In Mexico, the incidence and prevalence of the disease is little studied, however, it is estimated that 3.5 out of every 100,000 inhabitants suffer from it. In this way, it represents the second and fifth cause of mortality in groups of 0 to 18 years and 18 to 29 respectively.
The cause of the tumors is uncertain, according to Dr. Tsz Lau, a board-certified neurosurgeon at Houston Methodist Hospital. However, according to information shared by the Houston Methodist, scientific advances have managed to find risk factors. These factors include the family history of patients and exposure to ionizing radiation.
Like other tumors, brain tumors can be benign or malignant, that is, cancerous. Although benign brain tumors grow slowly and do not invade surrounding tissues, they can put pressure on sensitive areas of the brain. The pressures can cause serious health problems, which may require treatment and scientific advances.
For their part, malignant brain tumors contain cancer cells and can be deadly, as they grow and invade healthy brain tissue. It is usually a secondary tumor, meaning cancer cells have migrated to the brain from another part of the body.
The symptoms presented by patients are difficulty in maintaining balance or walking, as well as progressive loss of sensation or movement in the arms or legs. Affected people may also have frequent and severe headaches, personality changes, seizures, speech difficulties and vision problems.
However, the statement consulted by this news agency highlighted that these symptoms can also be related to other neurological disorders. In this sense, scientific advances have managed to determine if you actually have a brain tumor through tools such as neurological tests to check alertness, balance, coordination and reflexes.
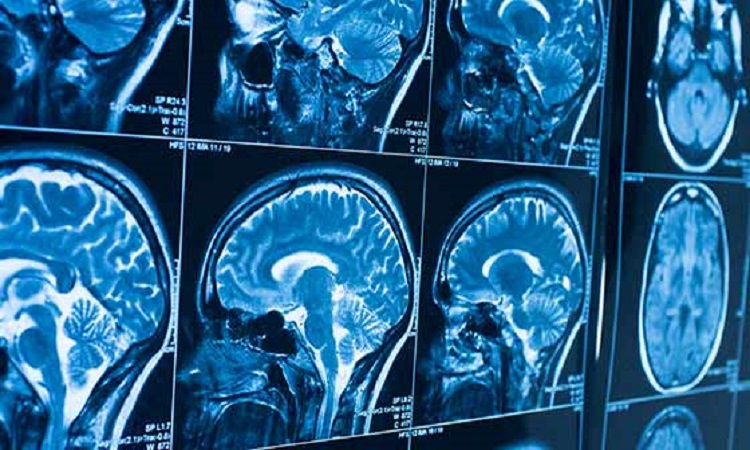
In addition, patients will be able to undergo more tests as a result of scientific advances in neurology, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or an MRI. Positron emission tomography (PET) scans or other brain scans may also be done. However, the diagnosis can only be confirmed with a biopsy.
For this part, the treatment of brain tumors is based on the factors of each patient, that is, age, general health and medical history. Likewise, the type of tumor, its location and size, as well as the probabilities for its spread, are considered.
According to the specialist at the Houston Methodist Hospital, therapies include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy or a combination of all. If it cannot be removed by surgery, other treatments can be applied to reduce or slow the growth of the tumor.
Among the most advanced treatments and therapies for tumors, according to Dr. Lau, are radiotherapy with X-rays, gamma rays or proteins, which destroy tumor tissue. Also, like any cancer, it can be treated with oral, injection or intravenous chemotherapy.
Other treatments and therapies include brachytherapy, which consists of radiotherapy seeds surgically placed after the tumor is removed. You can also opt for intraoperative chemotherapy or targeted therapy to attack the molecules involved in cell growth.
Likewise, it can be treated with portable devices, which produce electric fields and thus interrupt cell growth. Finally, there is surgery using magnetic resonance imaging to remove the largest number of malignant cells.
Experts continue to explore surgical techniques to remove brain tumors and find scientific advances to attack them. Dr. Lau concluded by commenting that the treatments are aggressive, but their prognosis gives patients hope.